What Is The Antiderivative Of 1 Cos 2x The antiderivative of a constant follows the same rules as the antiderivative of a power function Just picture the constant with a variable x raised to the power of 0 Any
Think of a simpler example if all we have available as elementary functions are polynomials or more generally rational functions the function 1 x wouldn t admit an elementary This means that int x x dx has no elementary antiderivative The specific reason to take mathbb Q x log x g as our differential field is that it is a field of trascendental
What Is The Antiderivative Of 1 Cos 2x

What Is The Antiderivative Of 1 Cos 2x
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Eaa0dksWv1I/maxresdefault.jpg
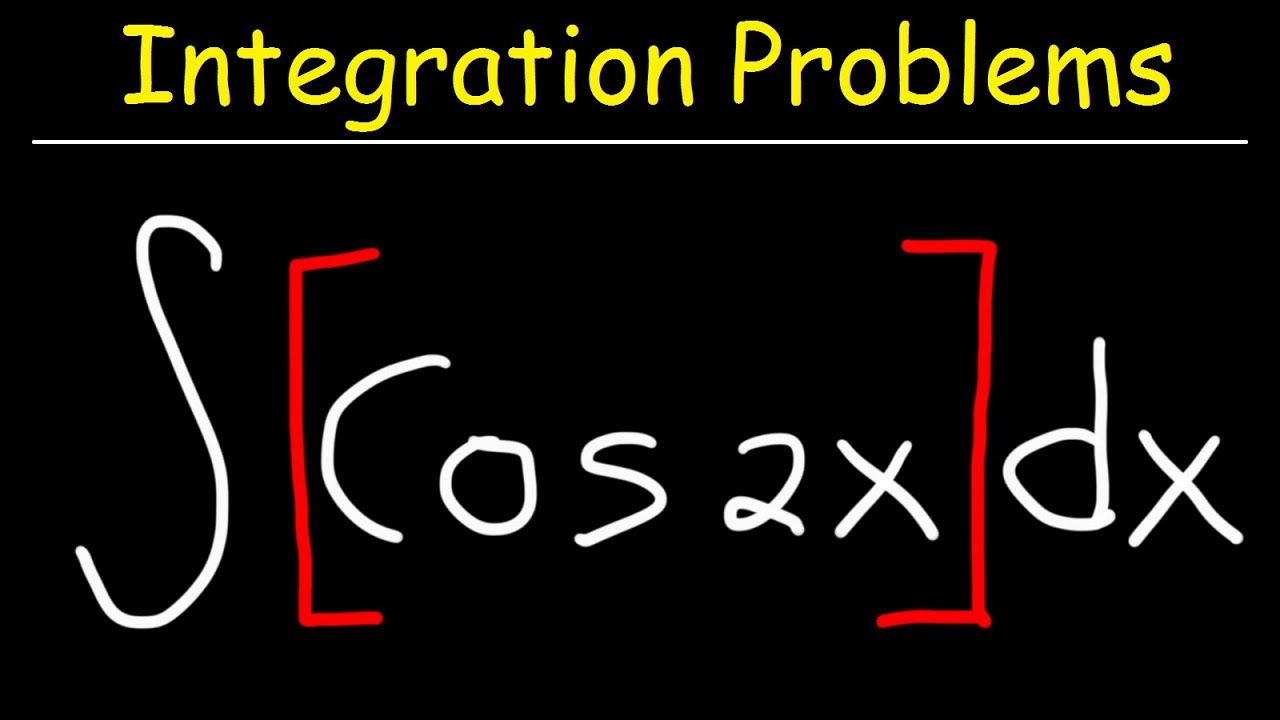
Integral Of Cos 2x YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/cCdj0uy0v80/maxresdefault.jpg

Antiderivative Of Ln x YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/B-Xw1RNMNYA/maxresdefault.jpg
Using indefinite integral to mean antiderivative which is unfortunately common obscures the fact that integration and anti differentiation really are different things in general Stack Exchange Network Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q A communities including Stack Overflow the largest most trusted online community for developers to learn share their
This is a contradiction and there is no antiderivative Edit I see you have edited your question so I will edit my answer Your second equation about winding numbers is true because of the The antiderivative of frac 1x is the function whose inverse is exactly equal to its own derivative
More picture related to What Is The Antiderivative Of 1 Cos 2x

Integral Of Sin 2x Integration Of Sin 2x Second Method YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/KpJxiiiJEUA/maxresdefault.jpg

Integral Of Cos 2x Substitution Method YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/4J2cLtyIEWI/maxresdefault.jpg
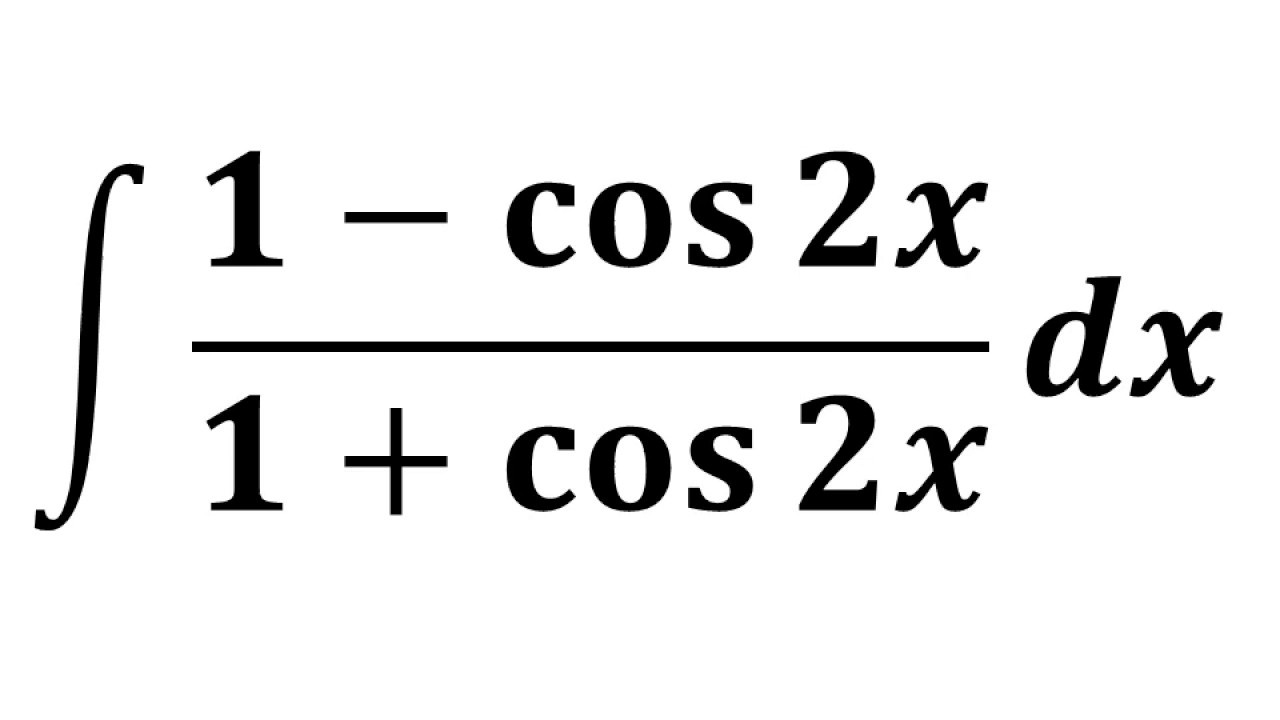
Integral Of 1 Cos 2x 1 Cos 2x YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/wfhXJqZDh8M/maxresdefault.jpg
One is the question of why the definite Riemann integral gives the correct notion of area under a curve for a nonnegative Riemann integrable function The other which As we know a non continuous function may have an antiderivative Thus the function may not be integrable That is although there is an explicitly defined antiderivative F x possibly not but
[desc-10] [desc-11]
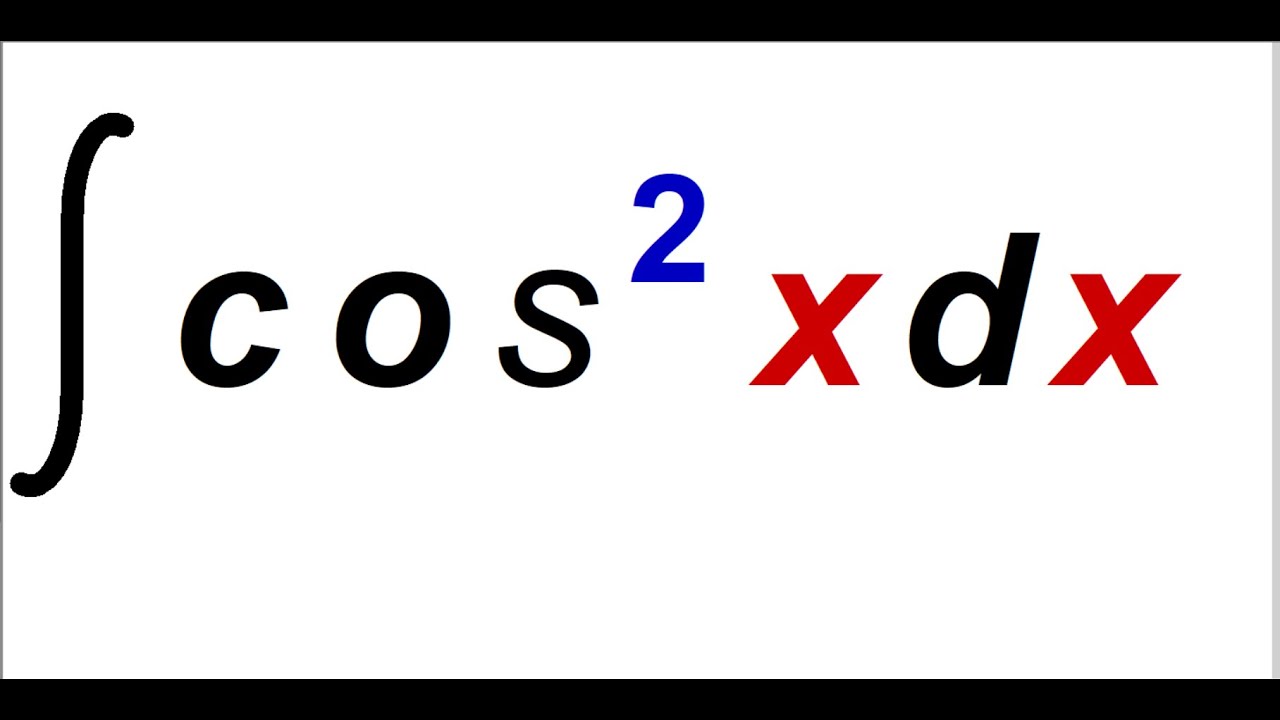
Integral Of Cosine Squared Integral Cos 2x YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/rTB6z7_7Vus/maxresdefault.jpg

6 8 Finding Antiderivatives And Indefinite Integrals Part 5
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/yt-tYfdy8gs/maxresdefault.jpg

https://study.com › academy › lesson › antiderivatives-of-constants-pow…
The antiderivative of a constant follows the same rules as the antiderivative of a power function Just picture the constant with a variable x raised to the power of 0 Any

https://math.stackexchange.com › questions
Think of a simpler example if all we have available as elementary functions are polynomials or more generally rational functions the function 1 x wouldn t admit an elementary

Integral Of Csc 2x cot 3x Calculus 1 YouTube

Integral Of Cosine Squared Integral Cos 2x YouTube

Integral E x Integral Of Exp x Antiderivative Of E x

Find The Most General Antiderivative Of 1 T T 2 sqrt t Check

Integration With U substitution The Antiderivative Of 1 x 2 sin 1 x
Antiderivative Rules
Antiderivative Rules
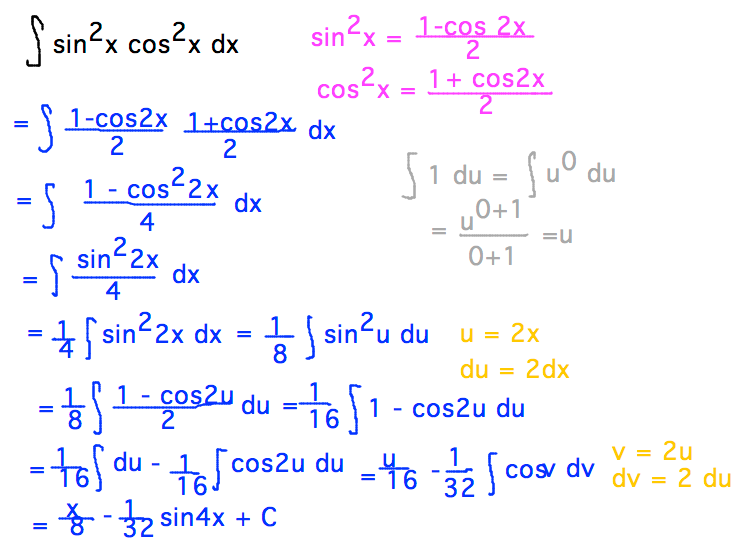
Geneseo Math 222 01 Integration
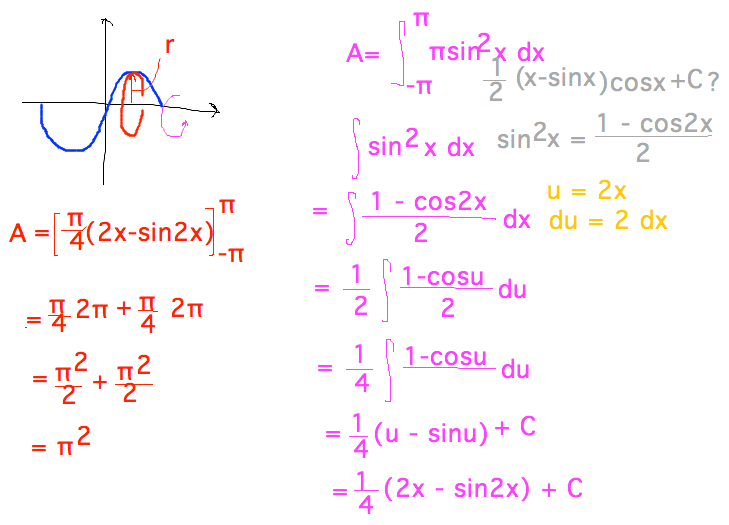
Geneseo Math 221 02 Volume 2

Ilectureonline
What Is The Antiderivative Of 1 Cos 2x - The antiderivative of frac 1x is the function whose inverse is exactly equal to its own derivative